
Adding workstations doesn’t impact network performance.Fast data transfers between workstations.When all data flows in one direction, the odds of having packet collision are eliminated.Also, bidirectional (two-way data travel) networks are possible. Most ring topologies are unidirectional, meaning that data can only move in one direction. In this network configuration, devices connect via a circular path, so each networked device is linked by two others in a “ring network.” So, when data packets transmit to one device, they have to travel through the ring until they’ve reached their destination. The more devices connected, the slower the network may become.If the central “bus” breaks down, your network goes down, which can leave you without access to important files and information at critical times.Requires less cable than some other topologies.Easiest topology for connecting computers and devices in a linear fashion.Bus topology (logical) network diagram example In other words, if the central “bus” breaks down, the entire network breaks down. Sometimes called line, linear, backbone or ethernet topology, a Bus topology connects each computer via a cable to a central “bus” with exactly two endpoints. To that end, let’s take a look at the most common types of topologies and the type of mapping that works best for each. And the kind of topology you choose can affect the performance and stability of your network, so it’s important to understand your options before diagramming your network. It’s worth noting that some types are better suited to physical mapping, while others work best for logical network diagrams. While there exists a wide range of derivations in topologies, they generally all stem from four basic formats: Bus, Ring, Star and Mesh. Topology refers to the arrangement of physical or logical aspects of your network. But which one you use, and when, all depends on your network topology. It shows all of the physical aspects and arrangement of the network, including ports, cables, racks and servers, as well as any other hardware or devices that apply.īoth types of network diagrams have their place, and you’ll probably use both. Think of physical network mapping like a floor plan. In logical network diagrams, there are pivots for small, medium and large networks, where network diagram templates can be helpful. It typically includes elements like subnets, network objects and devices, routing protocols and domains, voice gateways, traffic flow and network segments. LogicalĪ logical network diagram illustrates the flow of information through a network and shows how devices communicate with each other. Therefore, it’s essential to understand the differences so you can choose the right kind of mapping for each aspect of your organisation. There are two types of network diagramming, logical and physical. Send potential vendors RFPs without including sensitive or confidential information.

Document internal and external communication.Sell network-related projects to stakeholders.Outline the steps for completing a project.In addition, network mapping can help you:
PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL NETWORK DIAGRAM UPDATE
Whether you need to update an existing network or plan a new one, with the ability to visualise networks, you can see how and where interactions occur, track components and explore options. Example of a corporate network diagram Why use network diagramming Your organisation can utilise network diagrams as granular or as broad as needed, showing individual devices, a single application or just areas where services exist.
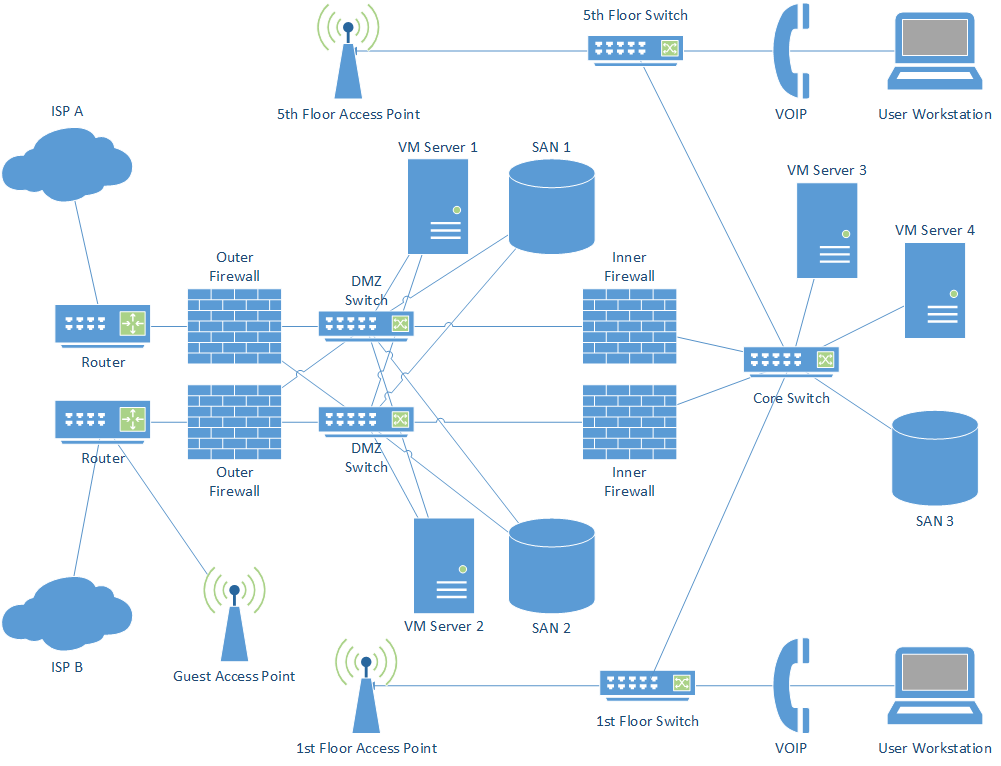

This blueprint acts as a road map to allow professionals to do things like understand and troubleshoot issues and errors, expand networks, and maintain security and compliance. Network diagrams help paint a picture of how these operational networks function and they identify components like routers, firewalls and devices, and visually show how they intersect. A network diagram will help organisations and teams visualise how devices like computers, and networks like telecommunications, work together.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
